Augmented reality rugs: everything retailers need to know
Blog -
Whether they’re used to shopping for home goods online or in-store, for customers, the process of purchasing a rug that suits their home can be a real challenge.
Not only do they have to decide what kind of rug they want, but they also need to ensure it matches their room decor and lifestyle and measure the area they want to put it in so that the rug they buy actually fits.
While many guides have been written on this subject, the truth is that customers still find it difficult to buy rugs without first seeing them in their own environment. Unsurprisingly, returns in the home furnishing industry are growing.
The good news is that rug retailers can overcome this problem with augmented reality (AR) technology. Research shows that 3D and AR technologies can decrease returns by as much as 25%. And while it was IKEA, with its Place app that pioneered furniture/furnishing visualisation at home, today, many homeware brands are using this technology to offer rug visualisation experiences to customers on their websites and apps.
Contrary to what some retailers may think, producing augmented reality rugs doesn’t have to be complicated or expensive. Thanks to easier access to 2D and 3D conversion technology, creating a catalogue of virtual rugs is now easier and more affordable than ever.
Here are just some ways brands can produce 2D, 3D and AR experiences for rugs, complete with real-life examples.
1. 2D rug visualisation with AR
To give shoppers an idea of how a specific rug would look in their space, some brands are giving potential customers access to 2D visualisation tools. With these tools, shoppers can superimpose a rug onto their floor, take a picture of it, and then adjust it.
While 2D visualisation is not real AR, in the sense that it doesn’t detect a customer’s floor and the digital rug doesn’t have any depth, it’s a more cost-effective way of showing prospective buyers how a rug would fit their home. This is because, with 2D visualisation, home furnishing companies don’t have to create 3D models of every single rug in their inventory. Rather, they can use the 2D images they already have.
For instance, before Houzz launched a 3D version of its “View in My Room” app (aptly called “View in My Room 3D”), it provided consumers with a 2D version of the feature.
According to Houzz’s Visual Technologies lead, Sally Huang, the mobile team would take product images, remove their background, and turn them into flat stickers. Because the team could do this to pretty much every photo in Houzz’s library, customers could visualise the company’s entire catalogue, including its extensive selection of rugs.

The 2D version of “View in My Room” was quite a success. In fact, as many as 1 in 2 shoppers who bought something from Houzz used the 2D version of “View in My Room”. Moreover, people who used the 2D visualisation tool spent three times more on the app than users who did not.
2. 3D rug visualisation
While 2D visualisation improves engagement and conversion rates, 3D visualisation is even more powerful.
Let’s look at Houzz again. Once it added 3D AR functionality to its “View in My Room” feature, Houzz discovered that shoppers were 11 times more likely to make a purchase after engaging with this feature. What’s more, buyers that use the 3D AR feature also tend to spend 2.7x times more than those that do not.
Today, MADE.com, Wayfair, and Target, among other home brands, all offer “View in your room” technology for rugs on their websites and apps. This technology, which uses Google’s Scene Viewer (Android) or Apple’s Quick Look (iOS), makes it possible for potential buyers to visualise rugs and other products in their own space with AR.
For instance, when buyers enable the “View in your room” feature from a rug product page on MADE.com, they are instructed to point their phone down at their floor and move it around slowly. If the room is bright enough, the selected rug will materialise in the customer’s room, and they will be able to take a photo or video of it.

Since this technology uses an existing Google solution rather than one that is built specifically for a particular brand, it is more cost-effective.
While the AR experience on MADE.com is available from users’ mobile browsers, in some cases, retailers may decide to incorporate this technology into an app. For instance, Wayfair customers can only enable the 3D rug visualisation feature from Wayfair’s app.

The downside of 3D rug visualisation through Google’s Scene Viewer (Android) or Apple’s Quick Look (iOS) is that this technology doesn’t always work very well, and rugs don’t always appear true to size.
3. White-label solutions for augmented reality rugs
Poplar Studio now offers white-labelled solutions for brands that want to enable their customers to visualise rugs with AR.
Incredibly easy to implement, our solution consists of a simple unit that can be embedded into any ecommerce website with a single line of code. It’s also affordable. Because we can build just a few base 3D models and use 2D images of the entire rug collection on top, we can manage 3D modelling very cost-effectively.
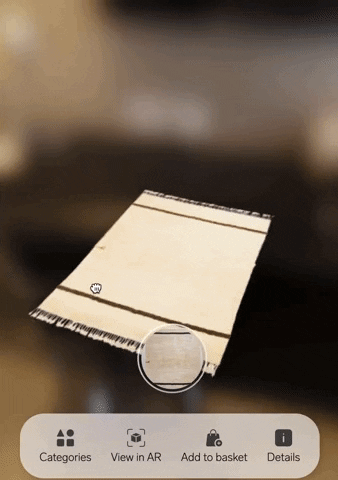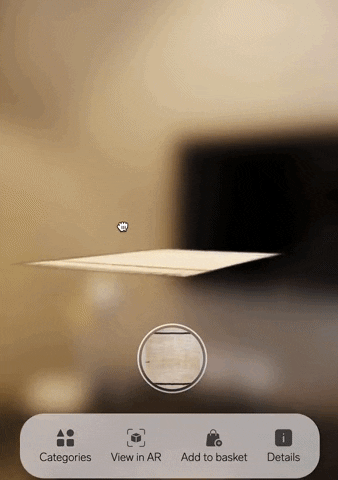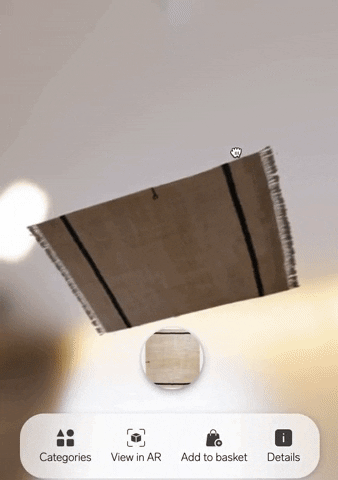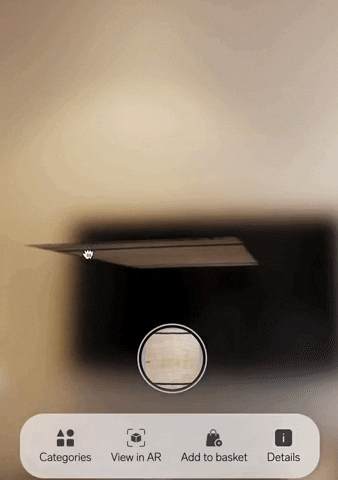
4. Interactive photos
Customers may not always be at home when shopping for a rug, but they may still want to double-check that the rug they’re eyeing fits their space. For this reason, some home brands provide a feature known as “Interactive Photos” to their customers.
For example, Wayfair’s “Interactive Photos” function, introduced in 2019, lets shoppers take a picture of their room and then see multiple products within it using overlays, even when they’re on the go.
Crucially, the technology behind this feature can understand the spatial information of a room from just a photograph. Amazon’s “Room Decorator” allows for a similar experience.
Notably, both retailers make it possible for customers to visualise more than one rug at the same time, a home interior trend that is largely popular.
5. AR portals
Brands that sell a variety of home furnishings and want to provide customers with inspiration on where and how to arrange rugs can create AR portals.
Portals are augmented windows or doors into different spaces and environments that users can interact with. In the home interior industry, AR portals are most commonly used to create virtual showrooms.
The AR portal we designed for MADE.com transported users into an Amsterdam-style apartment where they could see how a room was decorated with products from the brand’s catalogue, including rugs. Shoppers could “walk” through the apartment, even taking photos and videos of themselves as they did so.
Seeing how a particular room was decorated—and which rugs were placed where—users could better visualise how they could style their own homes.
Getting started with augmented reality rugs
AR is obviously becoming more popular among both businesses and consumers. Almost two in three leading consumer brands currently use this immersive technology, whereas 76% of consumers want to use AR as a “tool” in their day-to-day lives.
For any rug retailer that wants to better engage customers and reduce return rates, investing in AR is a no-brainer—especially now that it is possible to create realistic, to-scale augmented reality rug experiences without engaging in complex processes or inflating budgets.
Ready to integrate augmented reality rugs into your store? Get in touch with the team at Poplar Studio today.




